Ati Radeon Hd 4200 Driver What Product Family
| Release date | June 16, 2008 (June 16, 2008) |
|---|---|
| Codename | Radeon R700 serial M9x series |
| Architecture | TeraScale i |
| Transistors |
|
| Cards | |
| Entry-level | 4350, 4550, 4570 |
| Mid-range | 4650, 4670, 4730, 4750, 4770 |
| High-end | 4830, 4850, 4860, 4870 |
| Enthusiast | 4890, 4850X2, 4870X2 |
| API back up | |
| Direct3D | Direct3D x.1[one] Shader Model four.1 |
| OpenCL | OpenCL 1.1[2] |
| OpenGL | OpenGL 3.3[3] [iv] |
| History | |
| Predecessor | Radeon HD 3000 series |
| Successor | Radeon Hd 5000 serial |
The Radeon R700 is the engineering codename for a graphics processing unit of measurement series adult past Advanced Micro Devices under the ATI make name. The foundation flake, codenamed RV770, was announced and demonstrated on June sixteen, 2008 equally function of the FireStream 9250 and Movie theater ii.0 initiative launch media event,[5] with official release of the Radeon HD 4800 series on June 25, 2008. Other variants include enthusiast-oriented RV790, mainstream production RV730, RV740 and entry-level RV710.
Its direct competition was nVidia'southward GeForce 200 serial, which launched in the same calendar month.
Compages [edit]
This article is nigh all products nether the make "Radeon Hard disk drive 4000 Series". All products implement TeraScale one microarchitecture.
Execution units [edit]
The RV770 extends the R600's unified shader architecture past increasing the stream processing unit of measurement count to 800 units (upwardly from 320 units in the R600), which are grouped into ten SIMD cores composed of sixteen shader cores containing four FP MADD/DP ALUs and 1 MADD/transcendental ALU. The RV770 retains the R600's 4 Quad ROP cluster count, nonetheless, they are faster and now have dedicated hardware-based AA resolve in improver to the shader-based resolve of the R600 architecture. The RV770 also has x texture units, each of which can handle 4 addresses, xvi FP32 samples, and four FP32 filtering functions per clock cycle.[6]
Memory and internal buses [edit]
RV770 features a 256-bit memory controller and is the get-go GPU to support GDDR5 retention, which runs at 900 MHz giving an effective transfer rate of 3.6 GHz and memory bandwidth of up to 115 GB/s. The internal ring omnibus from the R520 and R600 has been replaced by the combination of a crossbar and an internal hub.[7]
Video acceleration [edit]
The SIP block UVD ii.0-ii.two implemented on the dies of all Radeon Hard disk 4000 Series Desktop gpus, 48xx series is using uvd 2.0, 47xx-46xx-45xx-43xx series is using uvd 2.2.
Support is available for Microsoft Windows at release, for Linux with Goad eight.10. The free and open-source commuter requires Linux kernel iii.x in combination with Mesa 9.1 (exposed via the widely adopted VDPAU)[8]), offering full hardware MPEG-two, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and VC-i decoding and the support for dual video streams, the Advanced Video Processor (AVP) also saw an upgrade with DVD upscaling capability and dynamic contrast feature. The RV770 series GPU as well supports xvYCC color space output and 7.1 surroundings sound output (LPCM, AC3, DTS) over HDMI. The RV770 GPU as well supports an Accelerated Video Transcoding (AVT) feature, which has video transcoding functions being assisted by the GPU, through stream processing.
GPU interconnect enhancements [edit]
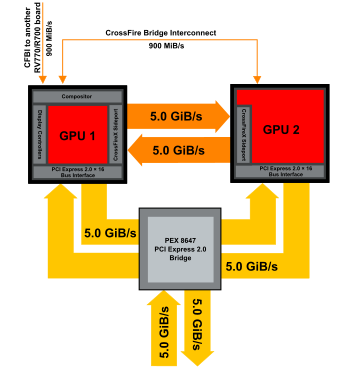
R700 inter-GPU communications compages
This generation of dual-GPU design retains the use of a PCI Express span, PLX PEX 8647 with a power dissipation of iii.8 watts inclusive of PCI Express 2.0 support, assuasive two GPUs on the same PCI Express slot with doubled bandwidth over the past generation of product (Radeon Hard disk drive 3870 X2). Subsequent generations of dual-GPU design also feature an interconnect for inter-GPU communications through the implementation of a CrossFire X SidePort on each GPU, giving actress 5 GB/due south full-duplex inter-GPU bandwidth. These two features increase total bandwidth for dual-GPU designs to 21.8 GB/due south.
OpenCL (API) [edit]
OpenCL accelerates many scientific Software Packages confronting CPU up to cistron ten or 100 and more. Open CL i.0 to 1.1 are supported for all Chips with RV7xx.[9]
Desktop products [edit]
Radeon HD 4800 [edit]
The Radeon Hard disk drive 4850 was announced on June 19, 2008 while the Radeon Hard disk 4870 was appear on June 25, 2008. They are both based on the RV770 GPU, packing 956 million transistors and being produced on a 55 nm procedure. The Radeon HD 4850 currently uses GDDR3 memory, while the Radeon HD 4870 uses GDDR5 retentiveness.
Another variant, the Radeon Hard disk 4830 was updated on October 23, 2008, featuring the RV770 LE GPU with a 256-bit GDDR3 memory interface, and 640 shader processors. Basically the RV770 LE is a RV770 with some functional units disabled.
Dual GPU products using ii RV770 GPUs, codenamed R700, were as well announced. One production named Radeon HD 4870 X2, featuring 2×1GB GDDR5 memory, was released on August 12, 2008, while another dual-GPU product, the Radeon HD 4850 X2, with GDDR3 memory and lower clock speeds, is also available.
A minor update was introduced on April 2, 2009 with the launch of Radeon Hard disk drive 4890 graphics cards based on the RV790 GPU. Featuring an improved blueprint with decoupling capacitors to reduce signal noise,[10] altered ASIC power distribution and re-timed the whole GPU chip, which resulted in a slight increase in dice size simply overall much improve stability at high clock rates and a higher default clock. On Baronial 18, 2009, AMD released a stripped down variant of the RV790 GPU chosen the RV790GT that is used by the Radeon Hard disk drive 4860 which is now available in all markets.
Radeon HD 4700 [edit]

The Radeon HD 4700 serial was announced on Apr 28, 2009. The Radeon HD 4770, is based on the RV740 GPU, packs 826 million transistors and existence produced on the latest forty nm process. The Radeon Hard disk 4730 was introduced June 8, 2009, unlike the RV740 based Radeon Hard disk 4770, the 4730 is a stripped downwardly 55 nm RV770 GPU, named the RV770CE. The 4730 packs 956 million transistors, and uses GDDR5 memory on a 128-bit bus. On September 9, 2009, the RV740PRO based Radeon Hard disk 4750 was released exclusively to the Chinese market. The Radeon HD 4750 is based on the 40 nm RV740 of the Radeon HD 4770 but features a lower clock speed and the absence of a half dozen-pin auxiliary power input.
Radeon Hd 4600 [edit]
The Radeon HD 4600 serial was announced on September 10, 2008. All variants are based on the RV730 GPU, packing 514 meg transistors and being produced on a 55 nm process. The PCIe version 4600 series products practise not require external power connectors.[11] [12] [13] [xiv] More recently, an AGP version of the 4670 has been released. This does require an external ability connector. As of March 2018, this elusive AGP bill of fare remains among the concluding cards using the aging bus.
Radeon Hd 4300/HD 4500 [edit]

The Radeon HD 4350 and Radeon Hard disk 4550 were appear on September 30, 2008, both based on the RV710 GPU, packing 242 million transistors and existence produced on a 55 nm process. Both products use either GDDR3, DDR3 or DDR2 video memory. AMD states these two products have maximum of 20 W and 25 W of ability consumption nether full load, respectively.[fifteen]
Chipset Table [edit]
Desktop Products [edit]
| Modelfour | Launch | Code name | Fab (nm) | Transistors (million) | Die size (mm2) | Bus interface | Clock rate | Core config1 | Fillrate | Retentivity2 | Processing power (GFLOPS) | TDP3 (Watts) | Crossfire support | API support (version) | Release Price (USD) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cadre (MHz) | Memory (MHz) | Pixel (GP/southward) | Texture (GT/s) | Size (MB) | Bandwidth (GB/due south) | Autobus type | Bus width (bit) | Unmarried precision | Double precision | Idle | Max. | Direct3D | OpenGL | OpenCL | ||||||||||
| Radeon Hard disk 4350 | Sep 30, 2008 | RV710 | 55 | 242 | 73 | PCIe 2.0 ×16 PCIe 2.0 ×ane AGP 8× | 600 | 400 650 | fourscore:8:4 | 2.40 | 4.fourscore | 256 512 1024 | vi.40 10.4 | DDR2 DDR3 | 64 | 92.0 | No | 20 | No | x.1 | 3.3 | 1.0 | ? | |
| Radeon Hard disk 4550 | Sep xxx, 2008 | RV710 | 55 | 242 | 73 | PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 600 600 | 655 800 | 80:8:4 | 2.40 | 4.80 | 256 512 1024 | ten.five 12.8 | DDR2 GDDR3 | 64 | 96.0 | No | 25 | ten.one | 3.three | 1.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon Hard disk drive 4570 | Nov 25, 2008 | RV710 | 55 | 242 | 73 | PCIe two.0 ×16 | 650 | 500 | 80:8:iv | 2.60 | five.20 | 1024 | 8.00 | DDR2 | 64 | 104.0 | No | 25 | x.1 | iii.3 | 1.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon Hd 4580 | Nov 20, 2011 | RV635 PRO | 55 | 378 | 135 | PCIe ii.0 ×16 | 796 | 693 | 120:8:4 | 3.18 | half dozen.37 | 512 | 22.2 | GDDR3 | 128 | 191.0 | No | 65 | 10.i | 3.3 | ane.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon Hard disk 4650 | Sep 10, 2008 | RV730 PRO | 55 | 514 | 146 | PCIe ii.0 ×16 AGP 8× | 600 650 | 400 - 500 500 700 | 320:32:8 | 4.80 5.20 | 19.2 20.8 | 256 512 1024 | 12.8 - xvi.0 16.0 22.4 | DDR2 GDDR3 GDDR4 | 64 128 | 384.0 416.0 | No | 48 | ii-Mode Crossfire | 10.1 | 3.three | 1.0 | ? | |
| Radeon HD 4670 | Sep x, 2008 | RV730 XT | 55 | 514 | 146 | PCIe ii.0 ×16 AGP eight× | 750 750 | 400 - 500 900 g | 320:32:eight | half-dozen.00 | 24.0 | 512 1024 | 12.8 - xvi.0 28.eight 32.0 | DDR2 GDDR3 GDDR4 | 128 | 480.0 | No | 59 | 10.1 | iii.three | 1.0 | 79 | ||
| Radeon Hd 4730 | Jun 8, 2009 | RV770 CE | 55 | 956 | 256 | PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 700 750 | 900 900 | 640:32:8 | five.sixty 6.00 | 22.4 24.0 | 512 | 57.six | GDDR5 | 128 | 896.0 960.0 | 179.2 192.0 | 110 | 10.1 | 3.3 | 1.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon HD 4750 | Sep 9, 2009 | RV740 | 40 | 826 | 137 | PCIe 2.0 ×sixteen | 730 | 800 | 640:32:16 | xi.vii | 23.4 | 512 | 51.2 | GDDR5 | 128 | 934.4 | 80 | 10.1 | 3.3 | one.0 | ? | |||
| Radeon Hd 4770 | Apr 28, 2009 | RV740 | 40 | 826 | 137 | PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 750 | 800 | 640:32:xvi | 12.0 | 24.0 | 512 | 51.two | GDDR5 | 128 | 960.0 | 192.0 | eighty | 10.1 | three.3 | 1.0 | 109 | ||
| Radeon HD 4810 | May 28, 2009 | RV770 CE | 55 | 956 | 256 | PCIe 2.0 ×sixteen | 625 750 | 900 900 | 640:32:8 | 5.00 half dozen.00 | xx.0 24.0 | 512 | 57.six | GDDR5 | 128 | 800.0 960.0 | 160.0 192.0 | 95 | 10.i | three.iii | 1.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon Hard disk 4830 | Oct 21, 2008 | RV770 LE | 55 | 956 | 256 | PCIe ii.0 ×sixteen | 575 | 900 | 640:32:16 | 9.20 | xviii.4 | 512 1024 | 57.6 | GDDR3 GDDR4 | 256 | 736.0 | 147.2 | 95 | 10.1 | 3.3 | 1.0 | $130 | ||
| Radeon HD 4850 | Jun 25, 2008 | RV770 PRO | 55 | 956 | 256 | PCIe ii.0 ×16 | 625 | 993 | 800:40:sixteen | 10.0 | 25.0 | 512 1024 2048 | 63.55 | GDDR3 GDDR4 GDDR5 | 256 | 1000 | 200.0 | 110 | 4-Way Crossfire | 10.1 | 3.3 | one.0 | 199 (149) | |
| Radeon Hd 4860 | Sep ix, 2009 | RV790 GT | 55 | 959 | 282 | PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 700 | 750 | 640:32:xvi | 11.2 | 22.4 | 512 1024 | 96 | GDDR5 | 256 | 896.0 | 179.2 | 130 | 10.one | 3.3 | i.0 | ? | ||
| Radeon HD 4870 | Jun 25, 2008 | RV770 XT | 55 | 956 | 256 | PCIe 2.0 ×xvi | 750 | 900 | 800:xl:sixteen | 12.0 | 30.0 | 512 1024 2048 | 115.2 | GDDR5 | 256 | 1200 | 240.0 | 150 | 10.1 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 299 (225) | ||
| Radeon HD 4890 | Apr 2, 2009 | RV790 XT | 55 | 959 | 282 | PCIe 2.0 ×xvi | 850 | 975 | 800:40:xvi | xiii.6 | 34.0 | 1024 2048 | 124.eight | GDDR5 | 256 | 1360 | 272.0 | 190 | 10.i | 3.iii | ane.0 | 249 | ||
| Radeon HD 4850 X2 | Nov 7, 2008 | R700 (2xRV770 PRO) | 55 | 956×ii | 256×2 | PCIe ii.0 ×xvi | 625 | 995 | 800:40:16×2 | 10.0×2 | 25.0×ii | 512×two 1024×2 | 63.7×2 | GDDR3 | 256x2 | 2000 | 400.0 | 250 | ii-Way Crossfire | ten.1 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 339 | |
| Radeon HD 4870 X2 | Aug 12, 2008 | R700 (2xRV770 XT) | 55 | 956×2 | 256×2 | PCIe two.0 ×16 | 750 | 900 | 800:40:sixteen×2 | 12×2 | 30×2 | 1024×2 | 115.2×2 | GDDR5 | 256x2 | 2400 | 480.0 | 286 | ten.ane | three.3 | i.0 | 449 | ||
| Model4 | Launch | Lawmaking proper noun | Fab (nm) | Transistors (million) | Die size (mm2) | Bus interface | Clock rate | Cadre config1 | Fillrate | Memory2 | Processing power (GFLOPS) | TDP3 (Watts) | Crossfire Support | API support (version) | Release Cost (USD) | |||||||||
| Core (MHz) | Memory (MHz) | Pixel (GP/s) | Texture (GT/s) | Size (MB) | Bandwidth (GB/s) | Bus type | Motorcoach width (bit) | Unmarried precision | Double precision | Idle | Max. | Direct3D | OpenGL | OpenCL | ||||||||||
one Unified shaders : Texture mapping units : Render output units
2 The effective information transfer rate of GDDR5 is quadruple its nominal clock, instead of double as information technology is with other DDR memory.
three The TDP is reference pattern TDP values from AMD. Different non-reference lath designs from vendors may lead to slight variations in bodily TDP.
iv All models feature UVD2 & PowerPlay.
IGP (Hard disk 4000) [edit]
- All Radeon HD 4000 IGP models include Direct3D 10.1 and OpenGL 2.0[16]
| Model | Launch | Lawmaking name | Graphics core | Fab (nm) | Transistors (1000000) | Die size (mm2) | Bus interface | Core clocktwo (MHz) | Core config1 | Fillrate | Memorythree | Processing power (GFLOPS) | Features / Notes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pixel (GP/s) | Texture (GT/s) | FP32 (GP/s) | Size (MB) | Bandwidth (GB/s) | Bus blazon | Constructive clock (MHz) | Autobus width (bit) | ||||||||||||
| Radeon HD 4200 Graphics (785G Chipset) | Aug 2009 | RS880 | RV620 | 55 | >205 | ~73 (~9 × eight.05) | HT 3.0 | 500 | 40:4:four | two | ii | i | Upwardly to 512 system + optional 128 sideport | 20.eight (system) + 2.6 (sideport) | HT (organisation) + DDR2-1066 DDR3-1333 (sideport) | 1333 (sideport) | 16 (sideport) | 40 | UVD2 |
| Radeon Hd 4250 Graphics (880G Chipset) | Mar 2010 | RS880 | 560 | 2.24 | 2.24 | 1.12 | HT (system) + DDR3-1333 (sideport) | 44.8 | |||||||||||
| Radeon Hard disk 4290 Graphics (890GX Chipset) | RS880D | 700 | 2.8 | two.viii | 1.4 | Up to 512 arrangement + 128 sideport | 56 | ||||||||||||
1 Unified shaders : Texture mapping units : Render output units
two The clock frequencies may vary in different usage scenarios, as ATI PowerPlay technology is implemented. The clock frequencies listed hither refer to the officially announced clock specifications.
3 The sideport is a dedicated memory bus. Information technology preferably used for frame buffer.
Radeon Characteristic Matrix [edit]
The following table shows features of AMD/ATI'due south GPUs (see also: List of AMD graphics processing units).
| Name of GPU serial | Wonder | Mach | 3D Rage | Rage Pro | Rage 128 | R100 | R200 | R300 | R400 | R500 | R600 | RV670 | R700 | Evergreen | Northern Islands | Southern Islands | Body of water Islands | Volcanic Islands | Arctic Islands/Polaris | Vega | Navi 1X | Navi 2X | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Released | 1986 | 1991 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | Apr 2000 | Aug 2001 | Sep 2002 | May 2004 | Oct 2005 | May 2007 | Nov 2007 | Jun 2008 | Sep 2009 | October 2010 | January 2012 | Sep 2013 | Jun 2015 | Jun 2016 | Jun 2017 | Jul 2019 | Nov 2020 | |||
| Marketing Name | Wonder | Mach | 3D Rage | Rage Pro | Rage 128 | Radeon 7000 | Radeon 8000 | Radeon 9000 | Radeon X700/X800 | Radeon X1000 | Radeon HD 2000 | Radeon HD 3000 | Radeon HD 4000 | Radeon HD 5000 | Radeon HD 6000 | Radeon HD 7000 | Radeon Rx 200 | Radeon Rx 300 | Radeon RX 400/500 | Radeon RX Vega/Radeon VII(7nm) | Radeon RX 5000 | Radeon RX 6000 | |||
| AMD support | | | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kind | 2nd | 3D | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Instruction set | Not publicly known | TeraScale pedagogy set up | GCN instruction set | RDNA education set | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Microarchitecture | TeraScale one | TeraScale 2 (VLIW5) | TeraScale three (VLIW4) | GCN 1st gen | GCN 2nd gen | GCN 3rd gen | GCN fourth gen | GCN fifth gen | RDNA | RDNA two | |||||||||||||||
| Type | Fixed pipeline[a] | Programmable pixel & vertex pipelines | Unified shader model | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct3D | North/A | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 8.i | ix.0 11 (9_2) | 9.0b xi (9_2) | ix.0c eleven (9_3) | ten.0 11 (10_0) | 10.i xi (10_1) | 11 (11_0) | eleven (11_1) 12 (11_1) | eleven (12_0) 12 (12_0) | xi (12_1) 12 (12_1) | xi (12_1) 12 (12_2) | ||||||||||
| Shader model | N/A | 1.4 | 2.0+ | two.0b | 3.0 | four.0 | 4.1 | 5.0 | five.1 | 5.one 6.3 | vi.4 | 6.5 | |||||||||||||
| OpenGL | N/A | ane.i | 1.two | i.iii | two.ane[b] [17] | iii.3 | 4.5 (on Linux: 4.5 (Mesa 3D 21.0))[18] [3] [four] [c] | iv.6 (on Linux: four.half-dozen (Mesa 3D xx.0)) | |||||||||||||||||
| Vulkan | N/A | 1.0 (Win seven+ or Mesa 17+) | i.ii (Adrenalin 20.one, Linux Mesa 3D twenty.0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| OpenCL | N/A | Shut to Metal | 1.1 (no Mesa 3D support) | i.2 (on Linux: 1.1 (no Image support) with Mesa 3D) | 2.0 (Adrenalin driver on Win7+) (on Linux: 1.1 (no Image support) with Mesa 3D, 2.0 with AMD drivers or AMD ROCm) | two.0 | 2.1 [19] | ||||||||||||||||||
| HSA / ROCm | N/A | | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Video decoding ASIC | N/A | Avivo/UVD | UVD+ | UVD two | UVD 2.2 | UVD 3 | UVD 4 | UVD iv.two | UVD 5.0 or half dozen.0 | UVD 6.3 | UVD 7[20] [d] | VCN 2.0[20] [d] | VCN 3.0[21] | ||||||||||||
| Video encoding ASIC | N/A | VCE 1.0 | VCE two.0 | VCE 3.0 or iii.1 | VCE iii.4 | VCE iv.0[xx] [d] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fluid Motion ASIC[east] | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ability saving | ? | PowerPlay | PowerTune | PowerTune & ZeroCore Power | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||
| TrueAudio | North/A | Via dedicated DSP | Via shaders | ? | |||||||||||||||||||||
| FreeSync | N/A | 1 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDCP[f] | ? | 1.4 | ane.4 ii.two | one.4 2.2 2.3 | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||
| PlayReady[f] | N/A | 3.0 | | 3.0 | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Supported displays[1000] | 1–2 | 2 | ii–6 | ? | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Max. resolution | ? | 2–half dozen × 2560×1600 | two–6 × 4096×2160 @ 30 Hz | 2–6 × 5120×2880 @ 60 Hz | three × 7680×4320 @ 60 Hz[22] | 7680×4320 @ 60 Hz PowerColor | |||||||||||||||||||
/drm/radeon [h] | | N/A | |||||||||||||||||||||||
/drm/amdgpu [h] | N/A | Experimental[23] | | ||||||||||||||||||||||
- ^ The Radeon 100 Series has programmable pixel shaders, but do not fully comply with DirectX 8 or Pixel Shader 1.0. See article on R100's pixel shaders.
- ^ R300, R400 and R500 based cards do not fully comply with OpenGL 2+ as the hardware does not support all types of non-power of two (NPOT) textures.
- ^ OpenGL 4+ compliance requires supporting FP64 shaders and these are emulated on some TeraScale chips using 32-bit hardware.
- ^ a b c The UVD and VCE were replaced by the Video Core Next (VCN) ASIC in the Raven Ridge APU implementation of Vega.
- ^ Video processing ASIC for video frame rate interpolation technique. In Windows information technology works as a DirectShow filter in your role player. In Linux, there is no support on the part of drivers and / or community.
- ^ a b To play protected video content, it as well requires carte du jour, operating organisation, driver, and application support. A compatible HDCP display is also needed for this. HDCP is mandatory for the output of certain sound formats, placing additional constraints on the multimedia setup.
- ^ More displays may be supported with native DisplayPort connections, or splitting the maximum resolution between multiple monitors with active converters.
- ^ a b DRM (Directly Rendering Manager) is a component of the Linux kernel. AMDgpu is the Linux kernel module. Support in this table refers to the most current version.
Mobile products [edit]
Graphics device drivers [edit]
AMD'southward proprietary graphics device driver "Catalyst" [edit]
AMD Catalyst is beingness developed for Microsoft Windows and Linux. Equally of July 2014, other operating systems are not officially supported. This may exist different for the AMD FirePro brand, which is based on identical hardware simply features OpenGL-certified graphics device drivers.
AMD Goad supports all features advertised for the Radeon brand.
The Radeon HD 4000 series has been transitioned to legacy support, where drivers volition be updated only to fix bugs instead of being optimized for new applications.[24]
Complimentary and open-source graphics device commuter "Radeon" [edit]
The free and open-source drivers are primarily developed on Linux and for Linux, merely accept been ported to other operating systems too. Each commuter is composed out of five parts:
- Linux kernel component DRM
- Linux kernel component KMS commuter: basically the device commuter for the display controller
- user-space component libDRM
- user-infinite component in Mesa 3D
- a special and distinct 2D graphics device driver for X.Org Server, which is finally almost to exist replaced by Glamor
The free and open-source "Radeon" graphics commuter supports most of the features implemented into the Radeon line of GPUs.[25]
The free and open-source "Radeon" graphics device drivers are not reverse engineered, just based on documentation released by AMD.[26]
See also [edit]
- AMD FirePro
- AMD FireMV
- AMD FireStream
- List of AMD graphics processing units
References [edit]
- ^ "Driver Support for AMD Radeon Hard disk 4000, HD 3000, Hard disk 2000 and older Series". AMD . Retrieved 2018-04-21 .
- ^ "AMD Catalyst 12.1 Treiber Download für AMD Radeon AGP Produktserie: AMD Radeon Hard disk 4xxx, AMD Radeon Hard disk 3xxx und AMD Radeon Hard disk drive 2xxx". AMD . Retrieved 2018-04-xx .
- ^ a b "Mesamatrix". mesamatrix.net . Retrieved 2018-04-22 .
- ^ a b "RadeonFeature". 10.Org Foundation . Retrieved 2018-04-20 .
- ^ AMD Stream Processor Outset to Suspension 1 Teraflop Barrier and AMD Demonstrates the Cinema 2.0 Feel
- ^ bit-tech.internet - RV770: ATI Radeon Hd 4850 & 4870 analysis | RV770 Graphics Architecture
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi & Derek Wilson (June 25, 2008). "The Radeon Hard disk drive 4870 & 4850: AMD Wins at $199 and $299". AnandTech.
- ^ Phoronix: AMD Releases Open up-Source UVD Video Support
- ^ https://world wide web.khronos.org/conformance/adopters/conformant-products
- ^ Jansen Ng (April 2, 2009). "ATI Launches Radeon Hard disk 4890; Over 50,000 Already Shipped". DailyTech.
- ^ Advanced Micro Devices - AMD Introduces the ATI Radeon Hd 4600 Series Graphics Cards for the Masses, Delivering Up To Double the Game Performance of the Contest at the Aforementioned Cost
- ^ Advanced Micro Devices - ATI Radeon Hard disk 4600 Series – Overview Archived 2009-03-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Softpedia - MSI Updates Radeon Hard disk drive 4600 Series with HDMI Support
- ^ tom's hardware - Radeon Hard disk 4600
- ^ Radeon Hd 4350 Graphics Technology - Overview Archived 2008-10-03 at the Wayback Machine and Radeon Hd 4550 Graphics Engineering science - Overview Archived 2008-10-03 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved October 3, 2008
- ^ "AMD RS880 Databook" (PDF).
- ^ "NPOT Texture (OpenGL Wiki)". Khronos Grouping . Retrieved 2021-02-10 .
- ^ "AMD Radeon Software Crimson Edition Beta". AMD . Retrieved 2018-04-twenty .
- ^ "AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT Specs". TechPowerUp . Retrieved 1 Jan 2021.
- ^ a b c Killian, Zak (22 March 2017). "AMD publishes patches for Vega support on Linux". Tech Report. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (xv September 2020). "AMD Radeon Navi two / VCN 3.0 Supports AV1 Video Decoding". Phoronix. Retrieved ane January 2021.
- ^ "Radeon's next-generation Vega architecture" (PDF). Radeon Technologies Group (AMD). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-09-06. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (7 Dec 2016). "The Best Features of the Linux iv.nine Kernel". Phoronix. Retrieved vii December 2016.
- ^ http://support.amd.com/en-us/download/desktop/legacy?product=legacy2&os=Windows%207%20-%2064
- ^ "RadeonFeature". Xorg.freedesktop.org. Retrieved 2014-07-06 .
- ^ "AMD Developer Guides". Archived from the original on 2013-07-xvi.
External links [edit]
- ATI Radeon HD 4000 Series: Desktop, Mobile
- techPowerUp! GPU Database
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radeon_HD_4000_series
Post a Comment for "Ati Radeon Hd 4200 Driver What Product Family"